카테고리 없음
4주차 리뷰
namu445
2022. 6. 6. 02:09
TypeORM - MySQL
더보기
- 관계형 데이터 베이스 사용을 도와주는 ORM의 하나
- 이번 프로젝트에서는 nestjs에 타입스크립트를 사용하기 때문에 nest와 호환이 좋은 TypeORM을 사용했다.
- Entity를 생성하고 스키마를 구성할 수 있다.
Entity 구성 예시
//Type ORM을 사용한 Entity 구성 예시
@Entity()
export class Product {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn('uuid')
id: string;
@Column()
name: string;
@Column()
description: string;
@Column()
price: number;
@Column()
isSoldout: boolean;
@JoinColumn()
@OneToOne(() => ProductSaleslocation) //뭐랑 연결할지, 1:1
productSalesloaction: ProductSaleslocation; //데이터 타입
@ManyToOne(() => ProductCategory) //Many 쪽에 JoinColumn이 포함되어있어 작성하지 않아도 된다.
productCategory: ProductCategory;
@ManyToOne(() => User)
user: User;
@JoinTable()
@ManyToMany(() => ProductTag, (productTags) => productTags.products) // M:N 테이블 설정
productTags: ProductTag[];Join 테이블 검색 예시
// Type ORM을 이용한 스키마 구성 후에 연결된 테이블 join 검색 설정
async findAll() {
return await this.productRepository.find({
relations: ['productSaleslocation', 'productCategory'], // join해서 검색하기
});
}M:N 외례키 등록 예시
async create({ createProductInput }) {
const { subCategoryId, brandId, modelId, ...product } = createProductInput;
const subCategory = await this.subCategoryRepository.findOne(
{
id: subCategoryId,
},
{ relations: ['mainCategory'] },
);
const brand = await this.brandCategoryRepository.findOne({
id: brandId,
});
const model = await this.modelRepository.findOne({ id: modelId });
const result = await this.productRepository.save({
...product,
subCategory: {
id: subCategoryId,
name: subCategory.name,
mainCategory: {
id: subCategory.mainCategory.id,
name: subCategory.mainCategory.name,
},
},
brand: {
id: brandId,
name: brand.name,
},
model: {
id: modelId,
name: model.name,
},
});
return result;
}TypeORM - graphQL
더보기
- nestjs는 graphQL을 지원하며 코드First 형식으로 작성할 수 있다.
@Entity() // Type ORM
@ObjectType() // GraphQL
export class Product {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn('uuid') // Primary Key 설정
@Field(() => String) //GraphQl 설정
id: string;
@Column({ default: false })
@Field(() => Boolean, { defaultValue: false })
isDeliver: boolean;
@ManyToOne(() => SubCategory)
@Field(() => SubCategory)
subCategory: SubCategory;
@JoinTable()
@ManyToMany(() => Color, (colors) => colors.products)
@Field(() => [Color])
colors: Color[];
}
// 리졸버 작성 예시
@Resolver()
export class ProductResolver {
constructor(private readonly productservice: ProductService) {} // 의존성 주입
@Query(() => Product) // 쿼리
fetchProduct(@Args('productId') productId: string) { // 인자 받기
return this.productservice.findOne({ productId });
}
@Mutation(() => Product) // 뮤테이션
createProduct(
@Args('createProductInput') createProductInput: CreateProductInput,
) {
return this.productservice.create({ createProductInput });
}
}물리 삭제, 논리 삭제
더보기
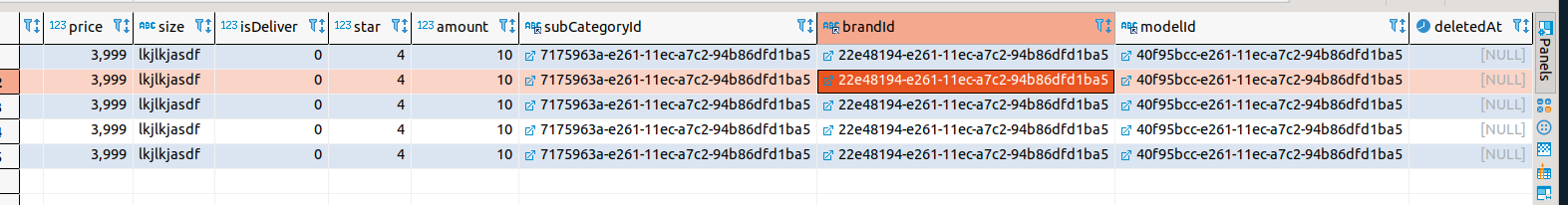
논리 삭제 예시 deletedAt 속성이 만들어져있다.
물리삭제
- DB에서 데이터 row를 완전히 삭제하는 것
논리 삭제
- DB에서 row를 완전히 삭제하지 않고 삭제 여부를 확인할 수 있는 속성을 만들어 삭제여부를 확인할 수 있게 하는 것

- 삭제한 정보를 복구할 필요가 있거나 따로 관리할 목적으로 사용한다.
- Type ORM은 DeletedDate 속성을 지정하는 데코레이터를 달아줄 수 있다.
@DeleteDateColumn()
deletedAt: Date;- 데코레이터를 달아주면 softDelete와 restore 기능을 간단하게 사용할 수 있다.
async delete({ productId }) {
const result = await this.productRepository.softDelete({ id: productId });
return result.affected ? true : false;
}
async restore({ productId }) {
const result = await this.productRepository.restore({ id: productId });
return result.affected ? true : false;
}회원가입 기능
더보기
쿠키, 세션
- 쿠키와 세션 방식에 대한 간단한 정리
쿠키, 세션
HTTP는 connectionless, stateless 특성을 가지고있음 쿠키와 세션은 이 특성으로 인한 문제를 보완하기 위해서 사용한다. connectionless 클라이언트가 요청에 응답을 받으면 연결을 끝는 특성 Keep-alive라는.
namu445.tistory.com
- 최근에는 쿠키와 세션방식 모두 JWT등을 이용한 토큰 방식을 같이 사용한다.
- 클라이언트 정보를 서버에 저장하고 인증을 진행하는 경우 서버의 부하를 줄이기 위해서 별도의 DB를 사용하기도 한다.
- 서버의 부하는 스케일 업이나 스케일 아웃으로 대응할 수 있지만 stateful 상태로 인한 문제를 해결하기 어렵다.
- 데이터를 디스크에 저장하는 DB(Mysql 등의 RDB)에 클라이언트 정보를 저장하기도 하지만 이 경우 서버에 부하가 늘어났던 것과 같이 DB에 부하를 줄 수 있기 때문에 REDIS와 같은 In-memory DB를 따로 사용하기도 한다.
- DB에서도 stateful 상태를 해결하기 어렵다. 때문에 아예 인증 DB를 따로 만들어 stateless 상태를 만든다.
- In-memory DB를 사용하면 디스크에 저장하는 것에 비해 속도도 빠르다.
- 휘발성은 문제가 되지 않는가? -> 인증 기록을 남기거나 관리하기 위해서 로그를 따로 저장하거나 인증 서버를 따로 두기도 한다.
DB의 사용자 테이블을 이용한 간단한 회원가입 기능
@Mutation(() => User)
createUser(
@Args('createUserInput')
createUserInput: CreateUserInput,
) {
return this.userService.create({ createUserInput });
}import { Field, InputType } from '@nestjs/graphql';
@InputType()
export class CreateUserInput {
@Field(() => String)
name: string;
@Field(() => Date)
birthDay: Date;
@Field(() => String)
phoneNumber: string;
@Field(() => String)
email: string;
@Field(() => String, { nullable: false })
password: string;
} async create({ createUserInput }) {
const { ...user } = createUserInput;
const hasUser = await this.userRepository.findOne({ name: user.name });
if (hasUser) {
return new ConflictException('이미 가입된 사용자입니다.');
}
const result = await this.userRepository.save({
...user,
});기타
더보기
시나리오에 맞는 에러 코드 return 방법
- nestjs에서는 상황에 맞는 에러코드를 간단히 보낼 수 있는 기능을 제공합니다.
// status 422
if (user === null) {
throw new UnprocessableEntityException('없는 사용자입니다.');
}
// status 409
if (hasUser) {
return new ConflictException('이미 가입된 사용자입니다.');
}Try Catch 기능을 대체할 수 있는 기능
- nestjs에서는 Try Catch를 글로벌 설정으로 간편하게 사용할 수 있는 기능을 제공한다.
app.useGlobalFilters(new HttpExceptionFilter());
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
import { Catch, ExceptionFilter, HttpException } from '@nestjs/common';
@Catch(HttpException)
export class HttpExceptionFilter implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: HttpException) {
const status = exception.getStatus;
const message = exception.message;
const response = exception.getResponse;
console.log('===========================================');
console.log('에러가 발생했어요!!');
console.log(`에러코드: ${status}`);
console.log(`에러메세지: ${message}`);
console.log(`에러내용: ${response}`);
console.log('===========================================');
}
}